Understanding Beta-Thalassemia: Importance of Early Detection and Screening Practices
Beta-thalassemia is a hereditary blood disorder characterized by reduced or absent synthesis of the beta chains of hemoglobin, leading to decreased production of functional hemoglobin. This condition affects millions of people worldwide, particularly those of
Beta-thalassemia is a hereditary blood disorder characterized by reduced or absent synthesis of the beta chains of hemoglobin, leading to decreased production of functional hemoglobin. This condition affects millions of people worldwide, particularly those of Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and Southeast Asian descent. While beta-thalassemia manifests in various forms, ranging from mild to severe, its impact on the quality of life can be significant if left undiagnosed or untreated.
In India, approximately 10,000 children are born with thalassemia every year, representing nearly 10% of global occurrences. India harbors one in eight thalassemia carriers globally, accounting for a staggering sum of nearly 42 million individuals carrying the β-thalassemia trait.1 The implementation of early prenatal screening holds the key to effectively managing thalassemia.
Role of early detection
Early detection plays a pivotal role in managing beta-thalassemia effectively. Detecting the condition at an early stage enables healthcare professionals to initiate appropriate interventions, thereby preventing complications and improving patients’ quality of life. Various screening practices are employed to identify individuals at risk of beta-thalassemia, with the use of hematology analyzers being a cornerstone in testing specific parameters.
Hematology analyzers are sophisticated instruments used to analyze blood samples for various hematological parameters, including red blood cell indices such as mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC). These parameters provide valuable insights into the size, shape, and hemoglobin content of red blood cells, aiding in the diagnosis of beta-thalassemia.
One of the primary screening methods for beta-thalassemia involves measuring the levels of hemoglobin and its components, particularly HbA2 and HbF. Hemoglobin electrophoresis, a technique commonly performed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or capillary electrophoresis, allows for the separation and quantification of different hemoglobin fractions. In individuals with beta-thalassemia trait or disease, elevated levels of HbA2 or HbF may indicate the presence of the condition.
Another screening approach involves assessing red blood cell indices, as abnormalities in these parameters can raise suspicion for beta-thalassemia. For instance, individuals with beta-thalassemia trait often exhibit microcytosis (reduced MCV), hypochromia (reduced MCHC), and anisocytosis (variation in red blood cell size). These characteristic changes in red blood cell morphology can be detected using automated hematology analyzers, which provide rapid and accurate results.
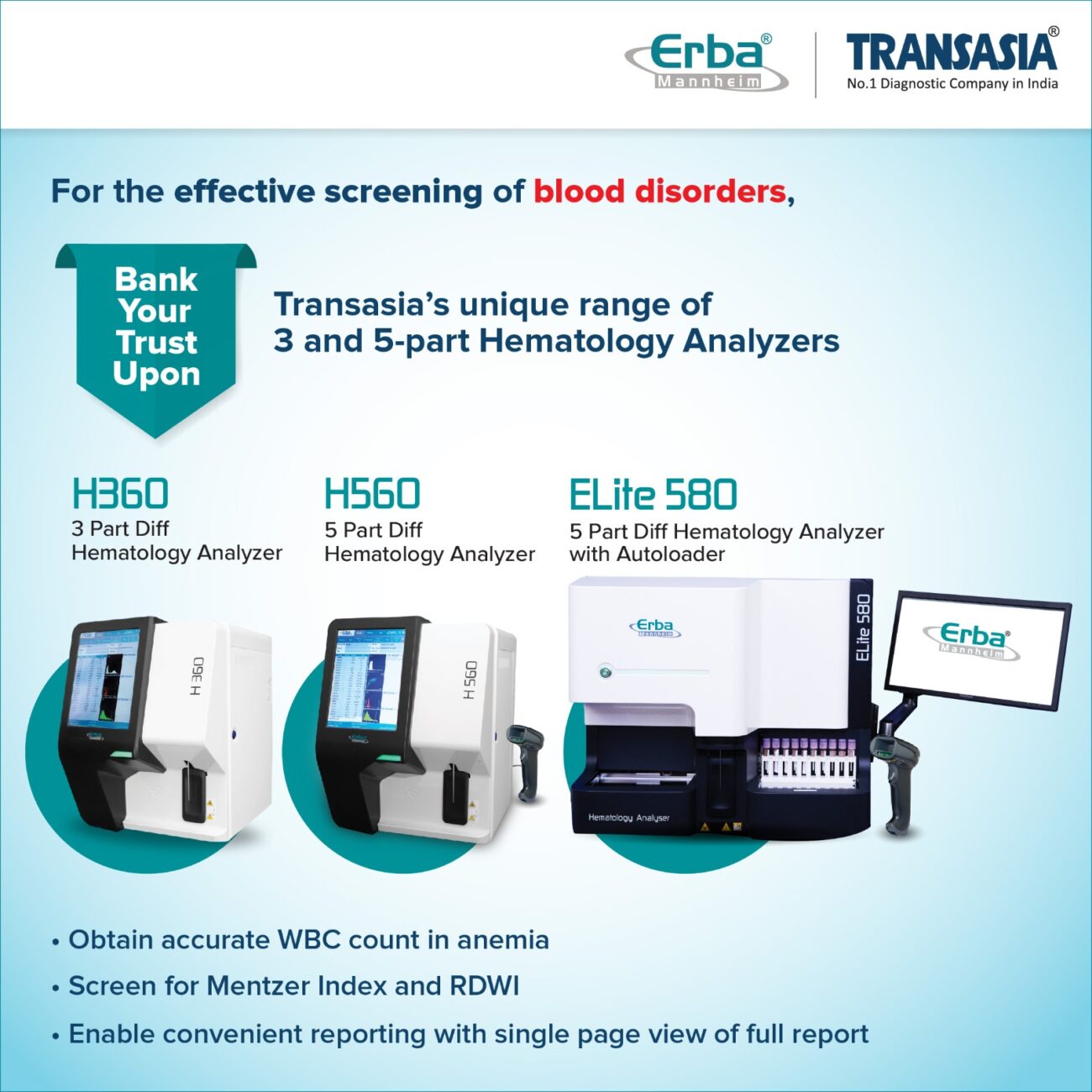
Transasia’s offerings for screening beta-thalassemia
At Erba Transasia, we are proud to present our advanced range of 3 and 5-part differential hematology analyzers, meticulously designed to elevate the standard of patient care, in screening of beta-thalassemia. Our latest software iteration introduces innovative parameters to the complete blood count (CBC), facilitating early detection of diseases such as iron deficiency and beta-thalassemia. Additionally, our recent groundbreaking feature – malaria flagging for P. vivax, helps enhance diagnostic capabilities.
Employing state-of-the-art Tri-angle Laser Flow Cytometry, our analyzers ensure unparalleled precision in white blood cell differentials. By discerning subtle variations through parameters like Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR), Red Cell Distribution Width Index (RDWI), and Mentzer Index, among others, our hematology analyzers transcend conventional testing, particularly in identifying abnormalities associated with blood disorders and cancers.
Comprehensive analysis is at the core of our offerings, with parameters including Platelet Large Cell Count (PLCC), Platelet Large Cell Ratio (PLCR), and Platelet Distribution Width-Standard Deviation (PDW-SD) meticulously examined. Furthermore, our analyzers boast a distinctive Auto Diluent Dispensing Mechanism for Pre-dilution, underscoring their indispensable role in modern diagnostics.
Early detection of beta-thalassemia is paramount for timely intervention and improved outcomes. Screening practices, including the use of hematology analyzers for testing specific parameters, play a crucial role in identifying individuals at risk of beta-thalassemia. By leveraging these screening tools and techniques, healthcare professionals can effectively diagnose beta-thalassemia, initiate appropriate management strategies, and provide comprehensive care to affected individuals and their families.






